Explore the Wonders of Bhutan
Your ultimate guide to the enchanting land of Bhutan, offering insights into its culture, landscapes, and travel tips.
Watt's Up? The Unseen Life of Batteries in Our Gadgets
Discover the hidden world of batteries! Uncover how these power sources fuel our gadgets and impact our daily lives. Recharge your curiosity!
How Do Rechargeable Batteries Work? Exploring Their Chemistry and Lifespan
Rechargeable batteries operate on the principle of reversible electrochemical reactions, allowing them to be charged and discharged multiple times. At the heart of these batteries lies an electrolyte, which facilitates the movement of ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging cycles. When a rechargeable battery is charged, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy, which gets stored in the battery. Upon discharging, this stored energy is released as electrical energy, powering devices such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Common types of rechargeable batteries include lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and lead-acid, each utilizing distinct chemical processes to store and deliver energy effectively.
The lifespan of rechargeable batteries largely depends on factors such as the chemical composition, usage patterns, and charging methods. Generally, most rechargeable batteries can endure hundreds to thousands of charge cycles before their capacity significantly diminishes. However, improper charging practices, like overcharging or exposing batteries to extreme temperatures, can accelerate wear and reduce longevity. Furthermore, maintaining optimal charging conditions and following manufacturer guidelines can enhance the lifespan of these batteries, ensuring they remain efficient and reliable for extended use.
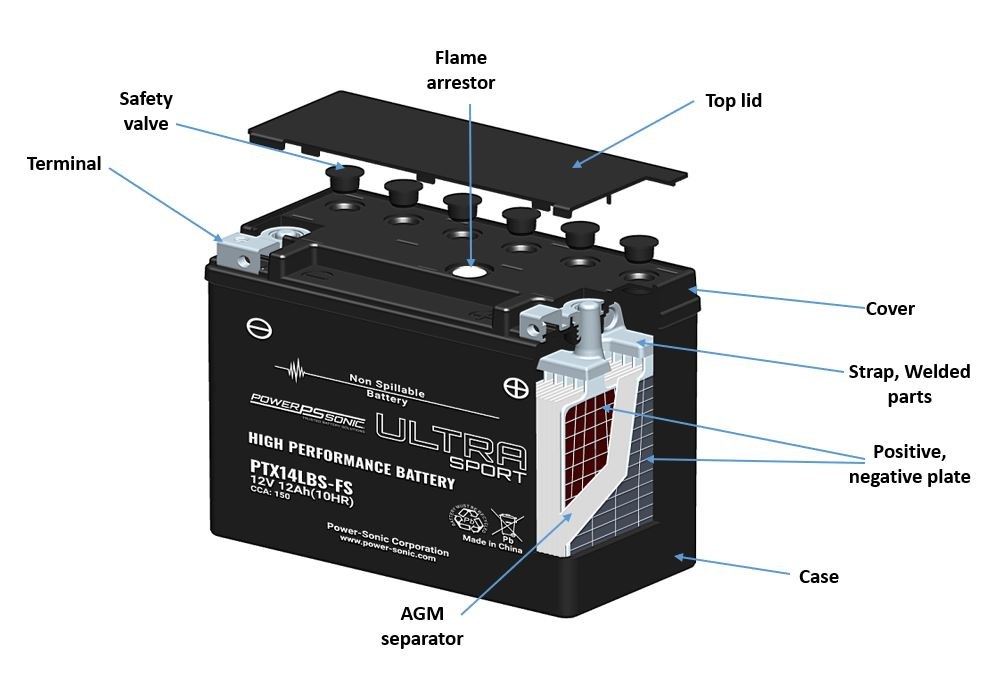
If you're looking for the best in portable sound, check out the Top 10 Bluetooth Portable Speakers that offer a perfect blend of sound quality, battery life, and portability. These speakers are ideal for outdoor adventures, parties, or even just relaxing at home. With various features such as waterproof designs and built-in voice assistants, there's sure to be a speaker that fits your needs.
The Hidden Impact of Battery Technology on Our Daily Devices
In today's fast-paced digital world, the role of battery technology in powering our daily devices cannot be overstated. From smartphones to electric vehicles, the advancements in battery efficiency and longevity have transformed the way we interact with technology. For instance, lithium-ion batteries have become the gold standard in mobile devices, enabling longer usage times and quicker charging. This innovation not only enhances user experience but also supports the increasing demand for renewable energy sources, as improved battery storage is crucial for harnessing solar and wind power.
Moreover, the hidden impact of battery technology extends beyond individual devices to broader environmental implications. As manufacturers continue to innovate, we are witnessing a shift towards sustainable materials and recycling processes that mitigate e-waste. The integration of batteries in smart homes, wearables, and IoT devices illustrates a growing reliance on this technology, further emphasizing the importance of responsible production and disposal methods. With the global push for sustainability, the future of battery technology holds promise not only for enhanced device performance but also for a cleaner, greener planet.
What Happens When Your Gadget’s Battery Dies? A Look at Energy Flow and Device Behavior
When your gadget's battery dies, it triggers a series of events that affect both energy flow and device behavior. Initially, the device experiences a sudden loss of power, leading to an immediate shutdown. This sudden cut in energy flow can cause a range of reactions depending on the device. For smartphones and laptops, the screen may go black, and any unsaved data could be lost. In contrast, simpler gadgets like remote controls tend to stop functioning without any significant consequences because they do not store data in the same way. Understanding these nuances is crucial for users determined to preserve their data and ensure the longevity of their devices.
Moreover, the way a device reacts to a dying battery often hinges on built-in management systems. Many modern gadgets come equipped with software that detects low battery levels and prompts users to save their work or switch to a power-saving mode. This energy flow management is designed to enhance device longevity and user experience. When the battery completely dies, the gadget may enter a protective state to prevent further damage. By comprehending these systems, users can make more informed decisions about battery maintenance and device usability. Therefore, knowing what happens when your gadget's battery dies is vital to enhancing your overall tech experience.